Introduction to Enterprise Architecture Planning
Definition according Spewak EAP (1992) is a process of defining the architecture to be able to support a number of business and plans to implement the architecture. In EAP there are a number of established architectural data architecture, application architecture, and technology architecture. EAP defines a set of business and architecture but not designing the system, database, or network.
EAP include increment and the second row of the first three columns in the Zachman Framework which includes columns of data, function, and tissue. Generated in the EAP is a blueprint (blue print) a high level of data, applications, and technologies for the entire enterprise to be used in the design and subsequent implementation.
EAP in the Zachman framework:
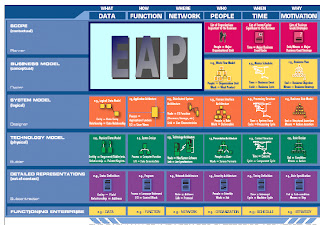
Stages in the EAP
From the above four stages, totalling eight components where each component are the stages and the results, as follows:

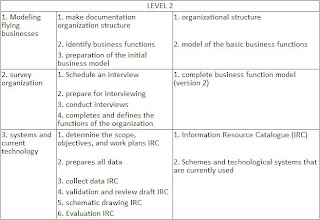
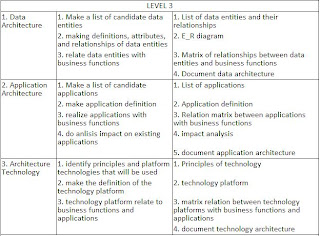

Business Modeling
In EAP, business modelling consists of two phases:
- Business modelling early
- Enterprise Survey
Guidelines to conduct business modelling early in the EAP are as follows:
- Define the major functional areas with the concept of "value added" Porter. Porter described the main activities, namely:
- Inbound Logistics : Associated with the receipt, storage and distribution of inputs into products
- Operation : All associated with transforming inputs into final product form
- Outbound Logistics : Associated with the collection, storage, physical distribution or customer service
- Marketing and Sales : Associated with the purchase of products and services users to encourage the user to buy or use the products made by the company
- Service : Associated with the provision of services to improve or maintain the value of a product such as installation, repair, training, supply of materials, maintenance and repair of technical guidance
- Firm Infrastructure : Activity costs and assets relating to the general management, finance, information systems security and safety, and other functions
- Human Resources Management : Activities involved such as receipts, hearings, training, development, compensation and development of skill levels of workers
- Research, Technology and System Development : Activities related to the costs associated with product R & DT, process improvement, equipment design, development of computer software, telecommunications system, a new database capabilities and support the development of computer-based systems
- Procurement : Functions associated with the purchase of inputs used in the Value Chain organization.
- For each functional area into sub-sub-functions by asking "What is this function?" Or "What is the meaning of the name of this function?"
- Continue until the sub-function decomposition functions obtained a single action, carried out repeatedly, produces output that is known, or can be linked to a specific organizational unit
- Assure the quality of the business model
- Connect with the detailed functions of the organizational unit that did it.
Support activities which Porter described as follows:





1 comments:
Great .
Post a Comment